What are the key components of Rigid flex pcb supplier?
key components of Rigid flex pcb supplier
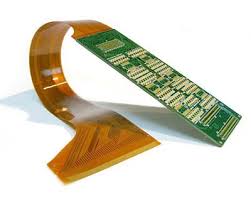
Rigid-Flex Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) represent a sophisticated blend of rigid and flexible circuit technologies, delivering enhanced design versatility and performance for advanced electronic applications. The manufacturing and supply of Rigid-Flex PCBs involve several critical components, each contributing to the overall functionality, durability, and reliability of the final product. Understanding these key components is essential for anyone involved in the design, production, or utilization of Rigid-Flex PCBs
The foundation of any rigid flex pcb supplier lies in its base materials. These include both rigid and flexible substrates. The rigid sections are typically made from FR-4, a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate known for its strength and stability. The flexible sections are usually constructed from polyimide, a material prized for its flexibility, thermal stability, and durability. These materials are carefully chosen to balance mechanical strength with the ability to bend and flex without damage.
Copper foil is essential for creating the conductive pathways on Rigid-Flex PCBs. It is laminated onto the base materials to form the electrical circuits. The thickness of the copper foil can vary depending on the specific electrical requirements and the design of the PCB. The copper layers must be precisely etched to create the intricate circuit patterns necessary for the board’s functionality.
What are the key components of Rigid flex pcb supplier?
Adhesives play a crucial role in bonding the different layers of a Rigid-Flex PCB. They are used to attach the flexible polyimide layers to the rigid FR-4 sections, as well as to secure the various copper layers in place. The choice of adhesive must consider factors such as thermal stability, mechanical flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors like moisture and chemicals. High-quality adhesives ensure the integrity of the layered structure throughout the lifecycle of the PCB.
Coverlays (or covercoats) are protective layers applied to the flexible circuits to shield them from environmental damage and mechanical wear. These layers, typically made from polyimide, provide insulation and protection for the underlying copper traces. They help prevent short circuits, improve the board’s mechanical strength, and enhance its overall durability. Proper application of coverlays is crucial for maintaining the reliability of the flexible sections.
Vias are small, plated holes that create electrical connections between different layers of the PCB. In Rigid-Flex PCBs, vias are essential for ensuring electrical continuity between the rigid and flexible sections. There are various types of vias, including through-hole vias, blind vias, and buried vias, each serving specific design purposes. Proper via design and plating are critical for the electrical performance and mechanical stability of the PCB.
The solder mask is a protective layer applied over the copper traces to prevent solder bridges and protect against environmental factors such as moisture and contaminants. In Rigid-Flex PCBs, the solder mask must be precisely applied to accommodate the unique design features of both rigid and flexible sections. It plays a key role in enhancing the durability and reliability of the solder joints and overall circuit integrity.
Surface finishes are applied to the exposed copper pads to protect them from oxidation and to ensure reliable soldering. Common surface finishes include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), and OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives). Each type of finish offers different advantages in terms of solderability, durability, and cost, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the application.
The final assembly of a Rigid-Flex PCB involves mounting electronic components and connectors onto the board. These components can include resistors, capacitors, ICs, and various types of connectors that interface with other electronic systems. The selection and placement of these components must consider factors like mechanical stress, thermal cycling, and the specific electrical requirements of the application.
To ensure the functionality and reliability of Rigid-Flex PCBs, comprehensive testing and quality assurance processes are essential. This includes electrical testing, such as continuity and insulation resistance tests, as well as environmental testing to simulate real-world conditions. Rigorous quality assurance procedures help identify and rectify any defects, ensuring that the final product meets the required standards and specifications.
In conclusion, the key components of Rigid-Flex PCB supplier include a combination of advanced materials, precise manufacturing techniques, and rigorous quality control processes. From the base materials and copper foils to adhesives, coverlays, vias, solder masks, surface finishes, and mounted components, each element plays a crucial role in the overall performance and reliability of the PCB. Understanding these components is vital for designing and manufacturing high-quality Rigid-Flex PCBs that meet the demanding requirements of modern electronic applications.